Main technologies utilized in frontend and backend.
Model-View-Controller architecture.
General research diagram with the three main procedure stage.
Implementation diagram with main modules and data dependence between them.
There are several opportunities to perform optimizations in high-level synthesis during scheduling, allocation and binding. These optimizations are highly multi-objective by nature, with conflicting objective functions. To deal with that scenario, it is necessary to apply multi-objective optimization algorithms. These algorithms maintain a trade-off between conflicting metrics. Multi-objective optimization is dedicated to solve problems in which a set of objective functions must be optimized simultaneously. We employ multi-objetive evolutionary algorithms to optimize delay, area, and power in the FPGA device.
Delay: is the total number of time steps or clock cycles. It is also called control step, timing, latency, or performance. This objective can be replaced by throughput, which is given as the ratio of the operating frequency to the latency multiplied by the input size.
Area: is the occupied components in the device, i.e. functional units plus registers. It is also called memory or space.
Power: is the power dissipation (dynamic power plus static power).
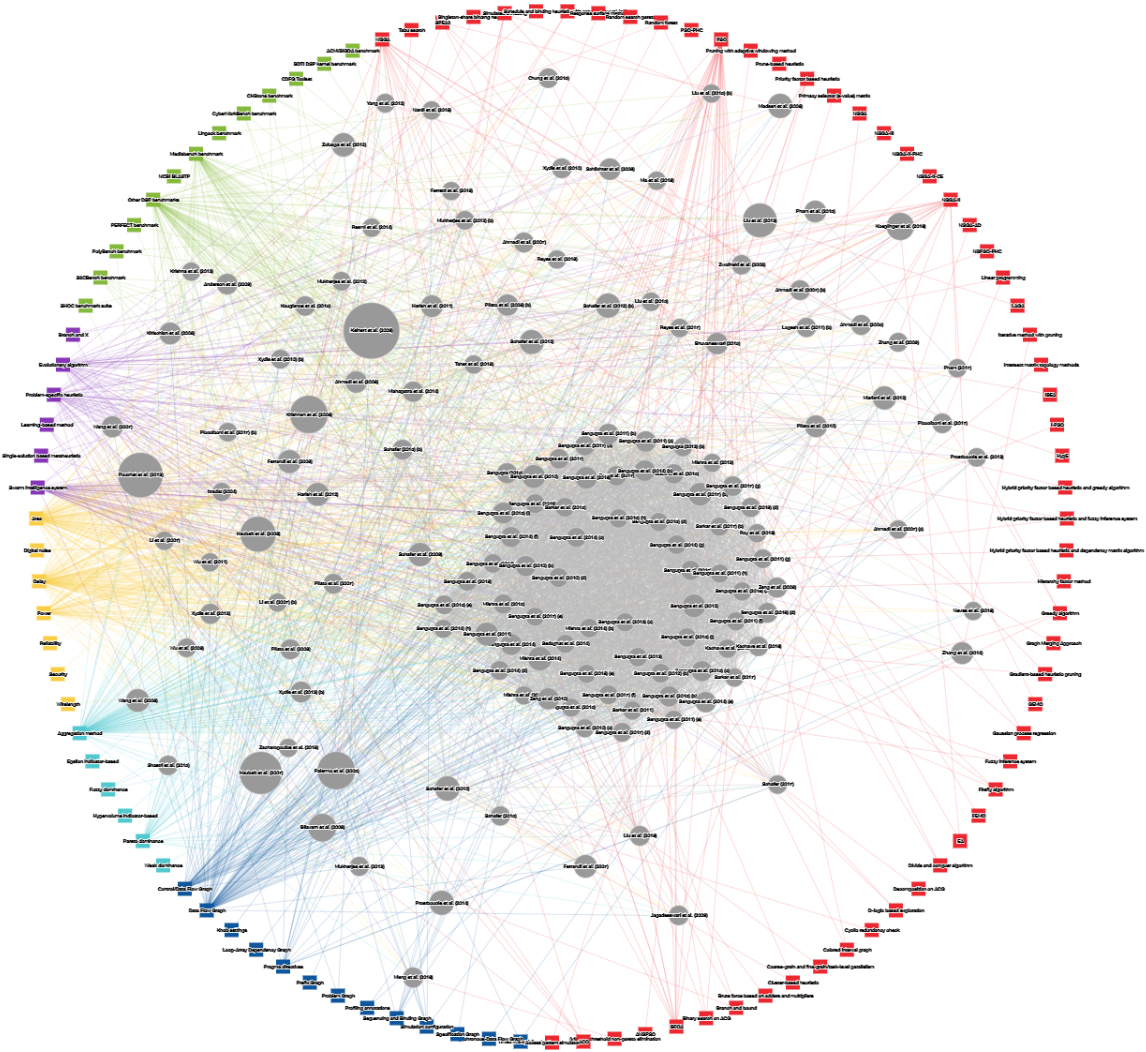
This network represents the state-of-the-art of Multi-Objective Optimization in High-Level Synthesis for FPGA devices. It was created through Cytoscape.js with Edge-weighted force directed layout.:
D. Reyes, and Y. Maldonado, “Comparison of Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms for High Level Synthesis in FPGA Devices”, Computación y Sistemas, Thematic Issue on Numerical and Evolutionary Optimization, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 425-437, 2018.
D. Reyes, J. C. Dibene, Y. Maldonado, and L. Trujillo, “High-Level Synthesis through metaheuristics and LUTs optimization in FPGA devices”, AI Communications, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 151-168, 2017.

VHDL by MOEA source code can be downloaded from the following GitHub repository:
https://github.com/darian16/vhdlbymoea

VHDL by MOEA is released under an GNU General Public License:
https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.html



